Last updated on 2025-11-23T21:04:08+08:00
1. TODO
2. 脑图
Xmind
Edraw
Hexo 地址
👉 http://blog.wangjia.ink/2025/11/03/源码:java.util.concurrent.FutureTask<V>源码解析/
3. 基础部分
3.1. FutureTask 概述
FutureTask 是一个具体类,继承了 java.util.concurrent.RunnableFuture<V>
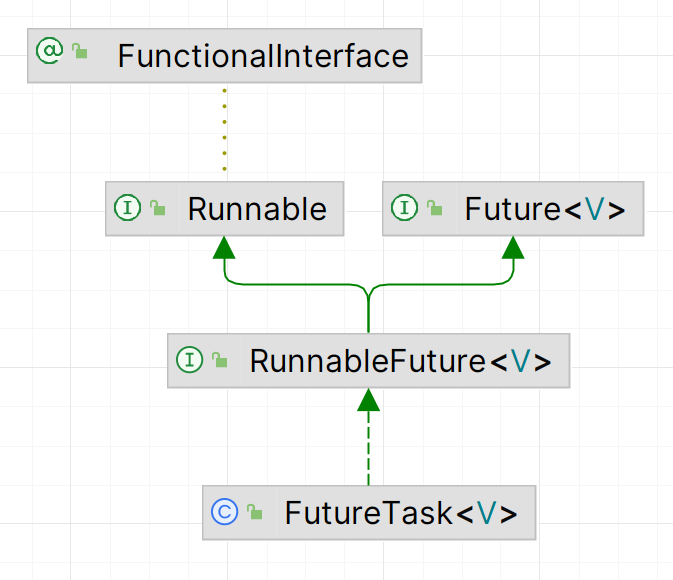
[!NOTE] 注意事项
- 详见源码:
RunnableFuture<V>
obsidian 内部链接:
- 源码:java.util.concurrent.RunnableFuture<V>源码解析
Hexo 链接:
- http://blog.wangjia.ink/2025/11/03/源码:java.util.concurrent.RunnableFuture<V>源码解析/
3.2. FutureTask 相关状态
NEW(0)
- 表示任务的初始状态
COMPLETING(1)
- 表示任务已经执行完毕,在赋值最终结果
- 这是一个非常短暂的瞬间状态
NORMAL(2)
- 表示任务正常退出
EXCEPTIONAL(3)
- 表示任务异常退出
CANCELLED(4)
- 表示任务已被取消
INTERRUPTING(5)
- 表示任务正在被停止
INTERRUPTED(6)
- 表示任务已被停止
[!NOTE] 注意事项
- 取消任务和停止任务还是有所区别的:取消任务是指取消那些尚未执行的任务。而停止任务则是任务正在执行时,你通过中断去让它停下来。如果任务能够响应中断,那就算是成功停止。但问题在于,如果任务没有响应中断,那么即使你发出了中断请求,它仍然会继续执行。所以 “停止任务” 并不一定能让它 “停止下来”
4. 内部类
4.1. WaitNode
FutureTask 的 WaitNode 链表就是由 WaitNode 构建的单向链表。所有因为调用 Future#get 而阻塞的 Thread 实例都会被投递到该队列
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| static final class WaitNode {
volatile Thread thread;
volatile WaitNode next;
WaitNode() { thread = Thread.currentThread(); }
}
|
5. 核心属性
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
private volatile int state;
private static final int NEW = 0;
private static final int COMPLETING = 1;
private static final int NORMAL = 2;
private static final int EXCEPTIONAL = 3;
private static final int CANCELLED = 4;
private static final int INTERRUPTING = 5;
private static final int INTERRUPTED = 6;
private Callable<V> callable;
private Object outcome;
private volatile Thread runner;
private volatile WaitNode waiters;
|
6. 构造方法
6.1. FutureTask(Callable<V> callable)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| public FutureTask(Callable<V> callable) {
if (callable == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
this.callable = callable;
this.state = NEW;
}
|
6.2. FutureTask(Runnable runnable, V result)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| public FutureTask(Runnable runnable, V result) {
this.callable = Executors.callable(runnable, result);
this.state = NEW;
}
|
7. 实例方法
7.1. 实例具体方法
7.1.1. 具体方法(实现)
7.1.1.1. Runnable 中接口方法的实现
7.1.1.1.1. void run()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| public void run() {
if (state != NEW ||
!RUNNER.compareAndSet(this, null, Thread.currentThread()))
return;
try {
Callable<V> c = callable;
if (c != null && state == NEW) {
V result;
boolean ran;
try {
result = c.call();
ran = true;
} catch (Throwable ex) {
result = null;
ran = false;
setException(ex);
}
if (ran)
set(result);
}
} finally {
runner = null;
int s = state;
if (s >= INTERRUPTING)
handlePossibleCancellationInterrupt(s);
}
}
|
7.1.1.2. Future 中接口方法的实现
7.1.1.2.1. boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| public boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning) {
if (!(state == NEW && STATE.compareAndSet
(this, NEW, mayInterruptIfRunning ? INTERRUPTING : CANCELLED)))
return false;
try {
if (mayInterruptIfRunning) {
try {
Thread t = runner;
if (t != null)
t.interrupt();
} finally {
STATE.setRelease(this, INTERRUPTED);
}
}
} finally {
finishCompletion();
}
return true;
}
|
7.1.1.2.2. boolean isCancelled()
1
2
3
4
5
| public boolean isCancelled() {
return state >= CANCELLED;
}
|
7.1.1.2.3. boolean isDone()
1
2
3
4
5
| public boolean isDone() {
return state != NEW;
}
|
7.1.1.2.4. get()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| public V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
int s = state;
if (s <= COMPLETING)
s = awaitDone(false, 0L);
return report(s);
}
|
7.1.1.2.5. get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| public V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException {
if (unit == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
int s = state;
if (s <= COMPLETING &&
(s = awaitDone(true, unit.toNanos(timeout))) <= COMPLETING)
throw new TimeoutException();
return report(s);
}
|
